
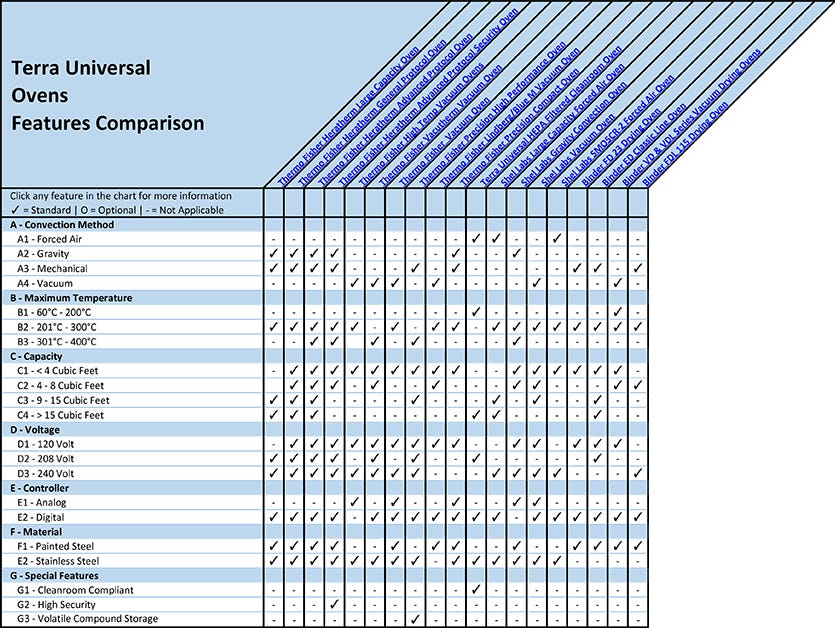
Laboratory and Cleanroom Ovens Feature Comparison
What is a Laboratory Oven?
Laboratory ovens are composed of a heating element connected to a sample storage chamber and regulated by an analog or digital controller. While the internal storage chamber is commonly made from chemical-resistant, 304-grade stainless steel, the oven exterior is regularly made from corrosion-resistant, durable powder-coated steel.
What are Laboratory and Cleanroom Ovens Used For?
Lab ovens are used to dry gently thaw frozen samples, cure composites and prepare raw materials. Commonly used in environmental labs, biotechnology facilities, pharmaceutical drug development, forensics labs, and raw material manufacturing plants, ovens are designed for general lab use or specialty applications, such as cGMP areas, ISO-rated cleanrooms, or fire-rated spaces.
A - Oven Convection Method
(back to chart)
A1 - Forced Air Ovens
Forced-air ovens utilize blowers located in a side-mounted or rear-mounted plenum to circulate high-velocity air across the sample storage chamber. The high-powered fans increase the air change rate within the internal chamber, to protect sample batches from cross-contamination, and optimize the heat transmission between air and sample. Forced-air ovens are commonly used to heat HPLC samples or rapidly dry glassware, such as beakers, Erlenmeyer flasks, and graduated cylinders.
A2 - Gravity Ovens
Gravity-convection ovens, which do not include a blower, are economical alternatives to mechanical-drying or forced-air ovens. Used primarily for general sample drying or material baking, gravity ovens must be closely monitored to ensure that cold spots or stagnant air zones don’t develop in corners of the internal chamber.
A3 - Mechanical Ovens
Mechanical-convection ovens utilize a blower or fan to circulate air throughout the internal chamber. The boost in air change rate supports faster recovery times after the door is opened and better temperature uniformity across the sample storage area.
What is the Difference Between a Mechanical and Gravity Oven?
Unlike gravity ovens, mechanical ovens are not prone to develop cold spots or stagnant air zones. However, mechanical ovens demonstrate lower temperature ramp rates and recovery times than forced-air ovens.
A4 - Vacuum Ovens
Vacuum ovens connect to an external vacuum pump to create a negative-pressure area within the sample storage chamber. An exhaust port vents moist and contaminated air away from the samples and through a filter for safe release.
What Are Vacuum Ovens Used For?
Vacuum ovens are commonly used for moisture determination, sample outgassing, desiccant regeneration, and hazardous sample processing.
Shop Vacuum Ovens by Convection Method
B - Maximum Lab Oven Temperature
(back to chart)
Standard laboratory ovens maintain temperatures ranging from ambient to 300°C.
High-temperature ovens utilize specialty heating elements and additional insulation to reach temperatures up to 400°C. Generally speaking, as the capacity and size of the oven increases, the maximum achievable temperature decreases. The lab oven’s intended use will define the required temperature range. For instance, curing and annealing processes commonly require heating to 250°C while glassware sterilization requires heating to 160°C.
C - Oven Capacity
(back to chart)
Compact, research-use lab ovens include 1 to 3 cubic feet of sample storage space.
Standard-capacity lab ovens commonly include between 4 and 9 cubic feet of internal storage space. High-capacity ovens boast sample storage capacities up to 28 cubic feet.
Terra’s Universal’s high-capacity, cleanroom-compliant oven includes 67 cubic feet of storage space and HEPA filtered air supply.
Shop Lab and Cleanroom Ovens by Size and Capacity
D - Lab Oven Voltage
(back to chart)
120-volt connections are suitable for standard laboratory power outlets in the United States.
208-volt or 240-volt connections require less current (amperage) and smaller conductors than equipment designed to operate at 120-volt.
E - Digital vs Analog Lab Oven Controls
(back to chart)
E1 - Analog Lab Ovens
Analog laboratory oven controllers include manual timers and temperature set point dials mounted on the front panel of the oven for convenient access. More economical than digital controllers, analog systems don’t include data export, interlocking doors, or digital, LED readouts.
E2 - Digital Lab Ovens
Digital laboratory oven controllers include an LED readout displaying current conditions, temperature set points, and programmed drying times. Certain digital controllers include over-temperature protection, open-door alarms, secure data export (for cGMP labs) and electronic door locks.
F - Laboratory Oven Material
(back to chart)
F1 - Painted Steel
Painted steel ovens are durable, long-lasting, corrosion-resistant, and able to withstand large fluctuations in ambient temperature and humidity. Common in manufacturing or general lab settings, painted steel ovens are commonly used for glassware drying, material stress testing, adhesive bonding, or glass annealing.
F2 - Stainless Steel
304-grade stainless steel lab ovens are is rigid, chemical-resistant, easy to disinfect, and maintain aseptic conditions within the lab. Stainless steel ovens are used primarily for electronics testing, circuit board production, petri dish sterilization, substrate adhesion, and forensic fingerprint analysis.
G - Special Features
(back to chart)
G1 - Cleanroom Compliant
Terra Universal’s high-capacity cleanroom oven includes dual HEPA filters installed above the internal chamber for uniform, laminar airflow and floor-level vents for optimal recirculation. The stainless steel unit, compatible with cleanrooms and cGMP areas, maintains ISO-5 conditions within the storage chamber.
G2 - High Security
Thermo Fisher’s Heratherm Advanced Protocol Security Oven includes an over-temperature alarm, high-security door lock, and open-door audio alarm.
Shop: Advanced Security Ovens
G3 - Volatile Compound Storage
Thermo Fisher’s Precision High-Performance oven is equipped with a rear-baffled blow-out panel for volatile material testing. The blow-out panel includes a retaining cage and positive-action door catch to prevent operator exposure to drug compounds or toxic substances.
Where Can I Buy Lab and Cleanroom Ovens Online?
Laboratory-Equipment.com is a specialty division of Terra Universal. For nearly 40 years, Terra Universal has served the life science, pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device markets. Customers appreciate a worldwide network of reps, factory-direct support, and ready-to-ship items available from Terra's manufacturing and warehouse facilities in Fullerton, California.
Shop laboratory ovens and accessories online for use in a wide variety of cleanroom, pharmaceutical, laboratory, and research environments.
Contact a Laboratory-equipment.com specialist through web chat, email, or phone for pricing or a same-day quote.
Terra Universal is the leading expert in the design and fabrication of ISO rated cleanrooms, furnishing and supplies.
Get a free consultation from one of our cleanroom specialists:
Call (714) 459-0731


